-
 Energy Crisis Risk Mitigation through Nuclear Power and RES as Alternative Solutions towards Self-Sufficiency
Energy Crisis Risk Mitigation through Nuclear Power and RES as Alternative Solutions towards Self-Sufficiency -
 How Do the Monetary Policy Shocks Shape the Housing Markets of New Zealand? A Natural Quasi-Experiment during the Pandemic
How Do the Monetary Policy Shocks Shape the Housing Markets of New Zealand? A Natural Quasi-Experiment during the Pandemic -
 The Moderating Effect of Perceived Risk on Users’ Continuance Intention for FinTech Services
The Moderating Effect of Perceived Risk on Users’ Continuance Intention for FinTech Services
Journal Description
Journal of Risk and Financial Management
Journal of Risk and Financial Management
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on risk and financial management, published monthly online by MDPI. The International Engineering and Technology Institute (IETI), Institute of Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (IDSAI), and International Research Institute for Economics and Management (IRIEM) are affiliated with the journal and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, EconBiz, EconLit, RePEc, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2022).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
The Optimal Level of Financial Growth in View of a Nonlinear Macroprudential Policy Regime Model: A Bayesian Approach
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 234; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040234 (registering DOI) - 07 Apr 2023
Abstract
A panel data analysis of nonlinear financial growth dynamics in a macroprudential policy regime was conducted on a panel of 10 African emerging countries from 1985–2021, where there had been a non-prudential regime from 1985–1999 and a prudential regime from 2000–2021. The paper
[...] Read more.
A panel data analysis of nonlinear financial growth dynamics in a macroprudential policy regime was conducted on a panel of 10 African emerging countries from 1985–2021, where there had been a non-prudential regime from 1985–1999 and a prudential regime from 2000–2021. The paper explored the validity of the inverted U-shape hypothesis in the prudential policy regime as well as the threshold level at which excessive finance boosts growth using the Bayesian Spatial Lag Panel Smooth Transition Regression (BSPSTR) model. The BSPSTR model was adopted due to its ability to address the problems of endogeneity and heterogeneity in a nonlinear framework. Moreover, as the transition variable often varies across time and space, the effect of the independent variables can also be time- and space-varying. The results reveal evidence of a nonlinear effect between finance and growth, where the optimal level of financial development is found to be 92% of GDP, above which financial development decreases growth. The findings confirmed the Greenwood and Jovanovic hypothesis of an inverted U-shape relationship. Macroprudential policies were found to trigger the finance–growth relationship. The policy recommendation is that the financial sector should be given adequate consideration and recognition by, for example, implementing appropriate financial reforms, developing a suitable investment portfolio, and keeping spending on technological investment in Africa’s emerging countries below the threshold. Again, caution is needed when introducing macroprudential policies at a low level of the financial system.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Perspectives of Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth in the Context of Sustainable Development)
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The Changes in the Perceptions of Women towards the Symbolic Value of Gold: Marketing and Financial Implications
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 233; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040233 (registering DOI) - 07 Apr 2023
Abstract
Gold is a sought-after good across the globe, particularly among Asian countries. The demand for gold is influenced by symbolic, utilitarian, and hedonic values. One of the critical values among these is symbolic value, which refers to the meanings associated with a commodity.
[...] Read more.
Gold is a sought-after good across the globe, particularly among Asian countries. The demand for gold is influenced by symbolic, utilitarian, and hedonic values. One of the critical values among these is symbolic value, which refers to the meanings associated with a commodity. This study attempts to identify the impact of cultural dynamism on the perceptions of women towards the symbolic value of gold. Cultural dynamism is a definite outcome of globalization; it refers to the changes in cultural beliefs and practices as an outcome of exposure to the elements of other cultures. These cultural changes will have an impact on the consumption of all types of goods, particularly those goods that are demanded due to a region’s culture. The present study attempts to identify the direction of cultural dynamics and its impact on gold in India as an outcome of the economy opening up in 1990. The perceptions of two sets of samples have been compared and contrasted in this study: one is a set of females born and married (this is because marriage has a vital role in determining perceptions towards gold) before the advent of globalization and its impacts in India, and the second set is the daughters (to ensure that other elements, such as socioeconomic aspects, are not affecting the perception) of the first set of customers. This study adopts a multidimensional scaling technique to analyze the data; this is due to the sound method that it is, and also due to the ability to provide a visual depiction of the outcomes. It could reveal evidence of polarization regarding perceptions towards the symbolic value of gold; it opened a research gap. A similar study with which to identify perceptions towards hedonic and symbolic values is suggested as an outcome of the study.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Financial Markets)
►▼
Show Figures
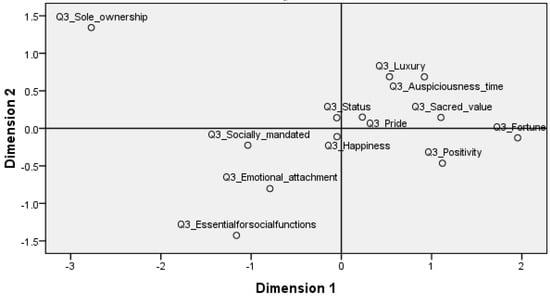
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Link between Bitcoin Price Changes and the Exchange Rates in European Countries with Non-Euro Currencies
by
, , , and
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 232; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040232 - 06 Apr 2023
Abstract
This paper contributes to the literature dedicated to the interlinkages between cryptocurrencies and currencies by investigating whether Bitcoin price movements affect the exchange rates of a sample of nine European countries with non-euro currencies. By resorting to the novel unconditional quantile regression, we
[...] Read more.
This paper contributes to the literature dedicated to the interlinkages between cryptocurrencies and currencies by investigating whether Bitcoin price movements affect the exchange rates of a sample of nine European countries with non-euro currencies. By resorting to the novel unconditional quantile regression, we show that there is a statistically significant link between Bitcoin price movements and changes in nominal exchange rates. In normal market conditions, an increase in the price of Bitcoin can be associated with an appreciation of the currencies from our sample, while during the COVID-19 pandemic, the relationship inversed. In addition, we find heterogeneities in this relationship, depending on the level of change in the nominal exchange rate. The results emphasize the relevance of Bitcoin price movements to the conduct of monetary policy through the exchange rate channel and that investors in cryptocurrencies and various financial assets denominated in the currencies from our sample can benefit from diversification by including both types of assets in their portfolios.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Future of Money: Central Bank Digital Currencies, Cryptocurrencies and Stablecoins)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure A1
Open AccessArticle
Environmental, Social, and Governance Considerations in WTI Financialization through Energy Funds
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 231; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040231 - 06 Apr 2023
Abstract
This study investigates interactions between energy funds and the oil market and examines the influence of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria in dynamic responses by fund managers and investors. We test for price and volatility transmission (also referred to as “spillover”) between
[...] Read more.
This study investigates interactions between energy funds and the oil market and examines the influence of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria in dynamic responses by fund managers and investors. We test for price and volatility transmission (also referred to as “spillover”) between energy funds and the oil market using recently developed econometric techniques. After identifying specific information flows, we investigate whether certain fund characteristics, including several ESG dimensions, are associated with the existence of information transmissions. Then, in logit regressions, we seek to identify if energy fund managers and their investors make decisions using information regarding ESG metrics, including fossil fuel involvement. The results confirm bidirectional price and volatility transmission between energy funds and the oil market, consistent with evidence of the financialization of energy markets that has been identified in recent studies. Several ESG dimensions are shown to influence investor sentiment and affect price and volatility interactions. Dynamic investor decisions in funds in reaction to oil prices do not appear to be strongly influenced by the fossil fuel involvement of the funds. Fund flows do appear to influence the oil market, with fund fossil fuel involvement being an important factor. This paper evaluates the impact of granular ESG characteristics on energy mutual fund flows, price, and volatility interactions with the oil market. While our results support the findings from previous studies, they also provide several new insights into the impacts of ESG criteria and investor behavior, particularly the dynamic response by fund managers and energy market investors related to the fossil fuel involvement of the funds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue ESG-Investing and ESG-Finance)
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Financial Technology on Improvement of Banks’ Financial Performance
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 230; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040230 - 05 Apr 2023
Abstract
This study investigates the main financial technologies adopted by banks to improve their financial performance. The study population consists of commercial banks listed on the Amman Stock Exchange and Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange, and includes financial information and data from 2012 to 2020.
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the main financial technologies adopted by banks to improve their financial performance. The study population consists of commercial banks listed on the Amman Stock Exchange and Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange, and includes financial information and data from 2012 to 2020. A total of 115 questionnaires, consisting of five questionnaires for each bank, were distributed to the study population in Jordan and the United Arab Emirates. The dependent variable is financial performance, while the independent variable is financial technology (FinTech). Multiple linear regression analysis was conducted to test the hypotheses. The results showed that FinTech has a positive effect on both total deposit and net profits. This study recommends that banks be encouraged to adopt inclusive strategies to attain sustainable development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Stability of Financial Markets and Sustainability Post-COVID-19)
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Remittance-Sending Countries’ Type on Financial Development in Recipient Countries: Can the Pandemic Make a Difference?
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 229; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040229 - 04 Apr 2023
Abstract
This study examines the effect of remittances on selected recipient countries’ financial development. Using weights for bilateral remittances from 1990 to 2015, this study calculates the weighted gross national income per capita of remittance-sending countries. This study then uses the weighted gross national
[...] Read more.
This study examines the effect of remittances on selected recipient countries’ financial development. Using weights for bilateral remittances from 1990 to 2015, this study calculates the weighted gross national income per capita of remittance-sending countries. This study then uses the weighted gross national income as an instrument to address the endogeneity between remittance and financial development. Using the instrument variable (IV) model, this study finds that remittances from low-skilled migrant-abundant sending countries have different effects than the highly skilled labor-abundant sending countries. Assuming the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries as a source of low-skilled and the Group of Seven (G7) as the source of high-skilled labor-abundant sending countries, remittance from relatively low-skilled emigrants has a greater impact on financial inclusion in the recipient countries than their high-skilled counterparts. In contrast, remittance from high-skilled countries has a greater impact on the development of the stock market. Similar types of effects of remittance on financial development have also been observed during the COVID-19 pandemic. The results suggest that policymakers should provide better foreign employment opportunities and improved transaction and investment policies in the home financial markets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Risk and Sustainability of Financial Markets, Institutions, and Enterprises in the Post COVID-19 Era)
►▼
Show Figures
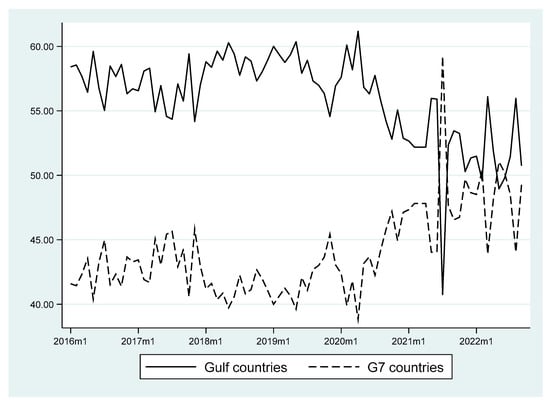
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Equity Investment Decisions of Operating Firms: Evidence from Property and Liability Insurers
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 228; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040228 - 04 Apr 2023
Abstract
During the 2007–2009 financial crisis, almost 10% of Property and Liability (P&L) insurers completely liquidated their equity portfolios, and more than half of them never resumed equity market investments. In contrast, those P&L insurers that continued investing in equities after the crisis, increased
[...] Read more.
During the 2007–2009 financial crisis, almost 10% of Property and Liability (P&L) insurers completely liquidated their equity portfolios, and more than half of them never resumed equity market investments. In contrast, those P&L insurers that continued investing in equities after the crisis, increased their portfolio allocation substantially. To understand these findings, we develop and estimate models that explain P&L insurers’ dynamic equity investment decisions, in terms of firm, group, and market characteristics over the period 2002–2018. We study three different approaches to equity investments, a pure investment strategy, internal capital market contributions, and an outsourcing option and find that the factors driving the decision to invest in equities differ from those that explain the extent of their equity investments. Moreover, we find that while equity portfolio losses drive the decision to temporarily cease investments in equities, the decision to permanently exit equity markets is driven by both equity market losses and underwriting losses. These findings shed some light on the factors driving the demand for equity investments by operating firms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Corporate Finance, Governance, and Social Responsibility)
►▼
Show Figures
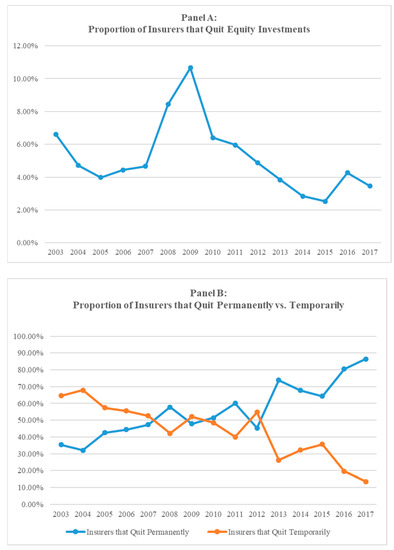
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Protect or Compete? Evidence of Firms’ Innovation from Import Penetration
by
and
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 227; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040227 - 04 Apr 2023
Abstract
This paper reassesses the long-debated relationship between market competition and firms’ innovation. While competition is traditionally measured at the industry level using historical data, our study utilizes two recently developed text-based measures of competitive threats which are forward-looking and constructed at the level
[...] Read more.
This paper reassesses the long-debated relationship between market competition and firms’ innovation. While competition is traditionally measured at the industry level using historical data, our study utilizes two recently developed text-based measures of competitive threats which are forward-looking and constructed at the level of individual firms. We address the potential endogeneity concerns and provide causal inference using instrumental variables including import tariffs and trade-weighted exchange rates, along with the propensity score matching (PSM) of firms that experienced exogenous shock from import competition. Our results show that an increase in competition unambiguously promotes firms’ innovation in terms of both quality and quantity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Global Business Strategy)
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Financial Market Analysis and Prediction with Emotion Corpora and News Co-Occurrence Network
by
and
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 226; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040226 - 04 Apr 2023
Abstract
This study employs an improved natural language processing algorithm to analyze over 500,000 financial news articles from sixteen major sources across 12 sectors, with the top 10 companies in each sector. The analysis identifies shifting economic activity based on emotional news sentiment and
[...] Read more.
This study employs an improved natural language processing algorithm to analyze over 500,000 financial news articles from sixteen major sources across 12 sectors, with the top 10 companies in each sector. The analysis identifies shifting economic activity based on emotional news sentiment and develops a news co-occurrence network to show relationships between companies even across sectors. This study created an improved corpus and algorithm to identify emotions in financial news. The improved method identified 18 additional emotions beyond what was previously analyzed. The researchers labeled financial terms from Investopedia to validate the categorization performance of the new method. Using the improved algorithm, we analyzed how emotions in financial news relate to market movement of pairs of companies. We found a moderate correlation (above 60%) between emotion sentiment and market movement. To validate this finding, we further checked the correlation coefficients between sentiment alone, and found that consumer discretionary, consumer staples, financials, industrials, and technology sectors showed similar trends. Our findings suggest that emotional sentiment analysis provide valuable insights for financial market analysis and prediction. The technical analysis framework developed in this study can be integrated into a larger investment strategy, enabling organizations to identify potential opportunities and develop informed strategies. The insights derived from the co-occurrence model may be leveraged by companies to strengthen their risk management functions, making it an asset within a comprehensive investment strategy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Neural Networks for Financial Derivatives)
►▼
Show Figures
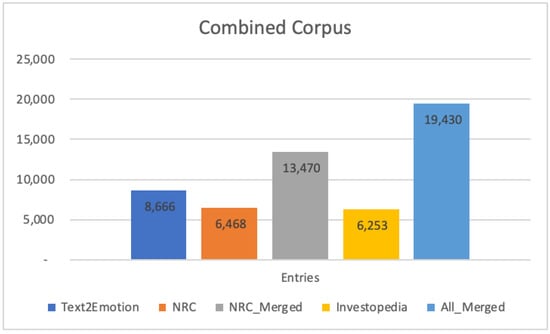
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Analysis of the Use of Accounting Information by Portuguese SMEs
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 225; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040225 - 04 Apr 2023
Abstract
Despite the significant economic contribution of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), little is known about the extent to which they make use of accounting information (AI). Although AI is considered one of the main sources of information for SMEs, many continue to ignore
[...] Read more.
Despite the significant economic contribution of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), little is known about the extent to which they make use of accounting information (AI). Although AI is considered one of the main sources of information for SMEs, many continue to ignore its potential, considering that this information is only intended to meet tax obligations. The literature stresses the influence of several factors on AI usage. However, the conclusions of the studies are fragmented, contradictory, and not very enlightening. Following these studies, the purpose of this paper is to explore which characteristics of decision makers, companies, and accounting services influence the importance and use of AI in SMEs. Data were collected through an online questionnaire survey applied to Portuguese SMEs. The findings show that the decision makers’ level of education, as well as their educational background, influence the importance they attribute to AI. It has also been found that smaller companies and SMEs that use outsourced accounting services make the least use of AI. Therefore, in addition to providing empirical evidence on the importance and use of AI, a debate that has been mainly theoretical, and on the importance of SMEs in any economy, this paper aims to raise awareness of the need to further study the decision-making process in such firms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial and Sustainability Reporting in a Digital Era)
Open AccessArticle
Investment Efficiency and Earnings Quality: European Evidence
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 224; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040224 - 03 Apr 2023
Abstract
This study aims to analyze the relationship between earnings quality and investment efficiency in the European context, in order to understand whether higher earnings quality mitigates investment inefficiencies. To further understand the relationship between earnings quality and investment efficiency, the roles of cash
[...] Read more.
This study aims to analyze the relationship between earnings quality and investment efficiency in the European context, in order to understand whether higher earnings quality mitigates investment inefficiencies. To further understand the relationship between earnings quality and investment efficiency, the roles of cash and financial constraints are also analyzed. We use firm-year data based on unbalanced panel data, and control for country, year, and industry fixed effects using a sample composed of listed and unlisted European companies from 19 countries and 17 industries for the period 2010–2018. The results show a positive and significant relationship between earnings quality and investment efficiency. In both scenarios of investment inefficiency, overinvestment and underinvestment, the results suggest that a higher quality of reported earnings mitigates investment inefficiencies. The results also suggest that the negative relationship holds for cash-constrained and unconstrained firms, and that in firms that are financially unconstrained (higher levels of cash and lower levels of leverage) the combined effect with earnings quality is associated with a lower investment efficiency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial Reporting, Accounting and Financial Statement Analysis)
Open AccessArticle
Measurement of Financial Competence—Designing a Complex Framework Model for a Complex Assessment Instrument
by
and
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 223; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040223 - 03 Apr 2023
Abstract
Financial competence is seen as a complex ability necessary for people to deal with personal financial issues on a daily basis. To foster young peoples’ financial competence via sophisticated and tailored educational programs, the identification of “competence gaps” through complex and authentic assessments
[...] Read more.
Financial competence is seen as a complex ability necessary for people to deal with personal financial issues on a daily basis. To foster young peoples’ financial competence via sophisticated and tailored educational programs, the identification of “competence gaps” through complex and authentic assessments is required. While a large number of assessment tools in the field of personal finance already exist, many of them suffer from different shortcomings concerning a competence-oriented approach. Therefore, we present an innovative way to assess students’ financial competence with a complex performance scenario about financial investment. The presented instrument is built on a specifically designed theoretical framework and addresses the need for holistic financial competence measurement. Results of pretesting trials indicate that the instrument is generally capable of measuring young learners’ financial competence, but challenges in scoring remain. Against this background, implications for the instrument’s iterative enhancement are presented and discussed with reference to validity and reliability properties, scoring issues, and statements about the overall feasibility of complex performance tasks in educational settings. The first draft of a scoring scheme is provided. The potential of the instrument in combination with modern technology-based measurement methods (eye tracking, emotion recognition) for competence assessment is described and suggestions for further research are outlined.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial and Economic Literacy—Implications for Education)
►▼
Show Figures
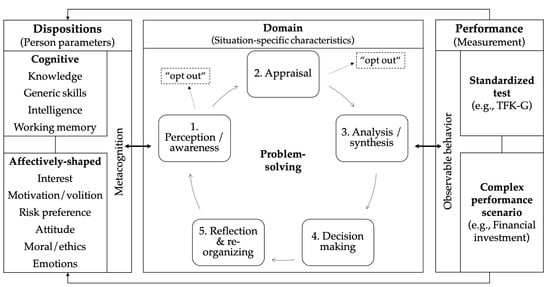
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Are Bitcoin and Gold a Safe Haven during COVID-19 and the 2022 Russia–Ukraine War?
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 222; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040222 - 02 Apr 2023
Abstract
Our investigation strives to unearth the best portfolio hedging strategy for the G7 stock indices through Bitcoin and gold using daily data relevant to the period 2 January 2016 to 5 January 2023. This study uses the DVECH-GARCH model to model dynamic correlation
[...] Read more.
Our investigation strives to unearth the best portfolio hedging strategy for the G7 stock indices through Bitcoin and gold using daily data relevant to the period 2 January 2016 to 5 January 2023. This study uses the DVECH-GARCH model to model dynamic correlation and then compute optimal hedge ratios and hedging effectiveness. The empirical findings show that Bitcoin and gold were rather effective hedge assets before COVID-19 and diversifiers during the pandemic and Russia–Ukraine war. From hedging effectiveness perspectives, gold and Bitcoin are safe-haven assets, and the investment risk of G7 stock indices could be hedged by taking a short position during thepandemic period and war except for the pair Nikkei/Gold. Additionally, gold beats Bitcoin in terms of hedging efficiency. We thus demonstrate the central role of Bitcoin and gold as financial market participants, particularly during market turmoil and downward movements. Our findings can be of interest to investors, regulators, and governments to take into consideration the role of Bitcoin in financial markets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Forecasting and Time Series Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
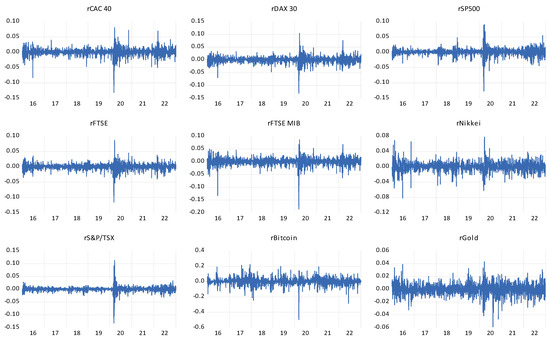
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Explaining Deep Learning Models for Credit Scoring with SHAP: A Case Study Using Open Banking Data
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 221; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040221 - 02 Apr 2023
Abstract
Predicting creditworthiness is an important task in the banking industry, as it allows banks to make informed lending decisions and manage risk. In this paper, we investigate the performance of two different deep learning credit scoring models developed on the textual descriptions of
[...] Read more.
Predicting creditworthiness is an important task in the banking industry, as it allows banks to make informed lending decisions and manage risk. In this paper, we investigate the performance of two different deep learning credit scoring models developed on the textual descriptions of customer transactions available from open banking APIs. The first model is a deep learning model trained from scratch, while the second model uses transfer learning with a multilingual BERT model. We evaluate the predictive performance of these models using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and Brier score. We find that a deep learning model trained from scratch outperforms a BERT transformer model finetuned on the same data. Furthermore, we find that SHAP can be used to explain such models both on a global level and for explaining rejections of actual applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Lending and Credit Risk Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Effects of Municipal Land and Building Policies on Apartment Size in New Residential Construction in Sweden
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 220; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040220 - 01 Apr 2023
Abstract
New residential construction in many countries with rapid urban growth is often interrelated with smaller housing units being built. Sweden is not an exception. It is of interest to investigate the driving forces behind this tendency. Our presumption is that municipal land price
[...] Read more.
New residential construction in many countries with rapid urban growth is often interrelated with smaller housing units being built. Sweden is not an exception. It is of interest to investigate the driving forces behind this tendency. Our presumption is that municipal land price policies and building permit regulations might play a certain role in this process. Contrary to previous studies that focus on the number of new dwelling units in housing construction, our purpose is to analyze the average size of new housing units and the factors that affect it on an aggregate level. We apply seemingly unrelated regressions for analysis of the average apartment size in new residential construction in the three largest metropolitan regions in Sweden as a function of the changes in population, apartment rent and prices, mortgage interest rates, land prices, and building permits per capita as a proxy for regulation. The unbalanced panel dataset includes the period between 1998 and 2017 and covers both the rental and the housing cooperative sectors. The analysis demonstrates that land prices and building policies along with market fundamentals are the underlying factors that affect the average size of an apartment in new residential construction in Sweden.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Shocks, Public Policies and Housing Markets)
►▼
Show Figures
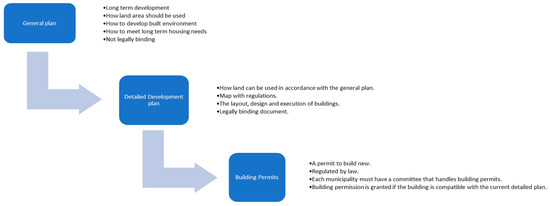
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Does the Size of the Business Still Matter, or Is Profitability under New Management, by Order of the COVID-19?
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 219; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040219 - 31 Mar 2023
Abstract
Businesses should come up with a strategy, plans, and goals so that their total assets can make a profit during the transformation process. Utilizing various features of a property can generate this income. This comparison provides evidence of profitability. During the global economic
[...] Read more.
Businesses should come up with a strategy, plans, and goals so that their total assets can make a profit during the transformation process. Utilizing various features of a property can generate this income. This comparison provides evidence of profitability. During the global economic downturn, a number of businesses encountered issues that caused their payment situations and profitability to deteriorate. The goal of this article is to ascertain whether particular profitability indicators also revealed the pandemic-related global crisis, particularly in the Visegrad Group countries. This analysis was conducted based on categories of business size. Specifically, 8671 enterprises were analyzed. The evaluation of indicators revealed whether there was a significant change in a negative direction, a significant change in a positive direction, or no significant change. It was possible to make a clear diagram of the companies that took part in the study and to figure out the median values in order to compare the results of the chosen profitability indicators. Correspondence analysis was conducted so that conclusions could be more accurate. According to the findings of this study, indicators of ROA, ROE, and ROS did not change significantly across enterprise size categories in the years preceding, during, and after the pandemic. Since the government regulations of the V4 countries had a significant impact on these businesses, the change was most obvious in the case of small businesses within the ROS indicator. The added value of the article is derived from its analysis of selected profitability indicators in the largest group of Central European nations and its relevance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Response of SMEs to Economic Changes in the Pandemic Era)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Impact of Proof of Work (PoW)-Based Blockchain Applications on the Environment: A Systematic Review and Research Agenda
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 218; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040218 - 31 Mar 2023
Abstract
Blockchain technology is being looked at to solve numerous real-world problems that demand transparency by meeting sustainable goals. Do we ponder whether this technology is a boon or a bane for the environment? This paper analyses blockchain’s dominant consensus method, Proof-of-Work (PoW), which
[...] Read more.
Blockchain technology is being looked at to solve numerous real-world problems that demand transparency by meeting sustainable goals. Do we ponder whether this technology is a boon or a bane for the environment? This paper analyses blockchain’s dominant consensus method, Proof-of-Work (PoW), which consumes more energy than Malaysia and Sweden and further deteriorates the environment through carbon emissions. This study is the first systematic evaluation of PoW consensus-based blockchain applications’ environmental consequences. We found 11 significant Theories, 6 Contexts, and 26 Methodologies (TCM) in 60 reviewed articles. We propose an Antecedents, Drivers, and Outcomes (ADO) model, which depicts that marginal profits drive high energy consumption and carbon emissions, with non-renewable energy proportionally responsible for carbon emissions. The article distinctively uses an integrated TCM-ADO framework for literature synthesis and the PESTLE framework for reporting future research areas. This is the first study to use the following four frameworks: PRISMA; TCM; ADO; and PESTLE for systematic literature review. Profit is identified as one of the most significant drivers of energy consumption and further carbon emissions. The article proposes 65 future research areas and makes theoretical contributions to the literature that may interest academicians, practitioners, and social stakeholders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Economy, Finance, and Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transparency and Disclosure and Financial Distress of Non-Financial Firms in India under Competition: Investors’ Perspective
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 217; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040217 - 29 Mar 2023
Abstract
Transparency and disclosure (T&D) of information trigger the interest of all stakeholders, including investors in a company. Cognizance of the company’s financial health before investing is very necessary. Disclosure of information in the firm’s financial reports reflects the firm’s financial performance. A firm’s
[...] Read more.
Transparency and disclosure (T&D) of information trigger the interest of all stakeholders, including investors in a company. Cognizance of the company’s financial health before investing is very necessary. Disclosure of information in the firm’s financial reports reflects the firm’s financial performance. A firm’s financial health protects investors’ and other stakeholders’ interests and the firm’s long-term sustainability. Owing to the importance of T&D and a firm’s financial health, this paper investigates the impact of T&D on the financial distress (FD) of non-financial firms (NFFs) listed in India. This study examines both linear and nonlinear connectivity of T&D and financial distress (FD). Their association is also investigated in a competitive scenario (under the moderating effect of competition). The panel data analysis is incorporated into the study having 78 NFFs as cross-sectional units with a timeframe from 2016 to 2020. Altman Z-score measures a firm’s FD (higher Z-score means low FD). BOS (Berger, Ofek and Swary) and AC (Almeida and Campello) scores are taken to consider investors’ perspectives of the firm’s FD. The T&D and Lerner indexes are used to assess the level of T&D and competition. The findings reveal that a higher T&D level decreases a firm’s financial stability or increases a firm’s FD. In nonlinear association, it is found that T&D has an inverted U-curved connection with financial stability or U-curved association with FD. It indicates that initially, higher T&D reduces FD, and after a threshold, it increases FD. However, under competition, T&D is not found to be significantly impactful for FD. The study is novel as no previous study has focused on such association under competition and taking investors’ perspective of a firm’s FD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Corporate Finance: Financial Management of the Firm)
►▼
Show Figures
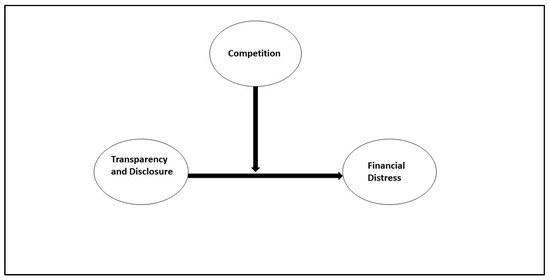
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predicting Cryptocurrency Fraud Using ChaosNet: The Ethereum Manifestation
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 216; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040216 - 29 Mar 2023
Abstract
Cryptocurrencies are in high demand now due to their volatile and untraceable nature. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Dogecoin are just a few examples. This research seeks to identify deception and probable fraud in Ethereum transactional processes. We have developed this capability via ChaosNet, an
[...] Read more.
Cryptocurrencies are in high demand now due to their volatile and untraceable nature. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Dogecoin are just a few examples. This research seeks to identify deception and probable fraud in Ethereum transactional processes. We have developed this capability via ChaosNet, an Artificial Neural Network constructed using Generalized Luröth Series maps. Chaos has been objectively discovered in the brain at many spatiotemporal scales. Several synthetic neuronal simulations, including the Hindmarsh–Rose model, possess chaos, and individual brain neurons are known to display chaotic bursting phenomena. Although chaos is included in several Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), for instance, in Recursively Generating Neural Networks, no ANNs exist for classical tasks entirely made up of chaoticity. ChaosNet uses the chaotic GLS neurons’ property of topological transitivity to perform classification problems on pools of data with cutting-edge performance, lowering the necessary training sample count. This synthetic neural network can perform categorization tasks by gathering a definite amount of training data. ChaosNet utilizes some of the best traits of networks composed of biological neurons, which derive from the strong chaotic activity of individual neurons, to solve complex classification tasks on par with or better than standard Artificial Neural Networks. It has been shown to require much fewer training samples. This ability of ChaosNet has been well exploited for the objective of our research. Further, in this article, ChaosNet has been integrated with several well-known ML algorithms to cater to the purposes of this study. The results obtained are better than the generic results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial Applications to Business and Financial Risk Management)
►▼
Show Figures
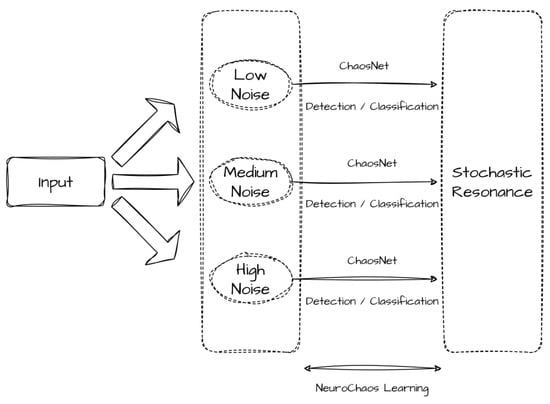
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Can Corporate Sustainability Drive Economic Value Added? Evidence from Larger European Firms
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2023, 16(4), 215; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16040215 - 29 Mar 2023
Abstract
This study analyses the association between firms’ sustainability and economic performance in Europe, considering the channels of margin and turnover. The sample is composed of firms listed in the STOXX Europe 600 Index from 2012 to 2020. The sustainability performance is captured by
[...] Read more.
This study analyses the association between firms’ sustainability and economic performance in Europe, considering the channels of margin and turnover. The sample is composed of firms listed in the STOXX Europe 600 Index from 2012 to 2020. The sustainability performance is captured by the combined and individual ESG scores from Refinitiv, and dynamically tested with proxies of economic performance, including economic value added, return on firms’ assets and its components, margin and turnover. The methodological approach comprises different panel data specifications and tackles the potentially unobserved, time-invariant heterogeneity, endogeneity concerns, and reverse causality biases. Our findings point to a strong positive association between firms’ sustainability and economic performance in Europe, although the individual ESG forces are not at play with the same intensity. The environmental pillar is the one that is systematically associated with better economic performance across all estimations. The influence of sustainability performance on economic performance is also channeled by both profit margin and turnover. We find that a 1% improvement in the ESG score yields an increase in the economic value added of 0.08%, EVA over revenues. In general, our findings point to a shift from the conventional business model perspective to the incorporation of a core sustainability proposition and agenda that brings advantages and drives economic performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial Reporting, Accounting and Financial Statement Analysis)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- JRFM Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Economies, JRFM, Mathematics, Sustainability, Data
Recent Advances and Applications in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM)
Topic Editors: María del Carmen Valls Martínez, José-María Montero, Pedro Antonio Martín CervantesDeadline: 31 July 2023
Topic in
Economies, IJFS, JRFM, Sustainability
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) Disclosure and Financial Markets
Topic Editors: Shaista Wasiuzzaman, Wan Masliza Wan MohammadDeadline: 24 December 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JRFM
Advances in Financial and Insurance Derivatives
Guest Editor: Thorsten RheinländerDeadline: 20 April 2023
Special Issue in
JRFM
Economics and Financial Networks and Their Impact on the Macroeconomy and Financial Markets
Guest Editors: Petre Caraiani, Mihail BusuDeadline: 30 April 2023
Special Issue in
JRFM
Corporate Finance and COVID-19
Guest Editors: Kainan Wang, Chune Young ChungDeadline: 20 May 2023
Special Issue in
JRFM
Empirical Corporate Finance
Guest Editor: Tao-Hsien Dolly KingDeadline: 30 May 2023














